FDA Approves First Topical Androgen Receptor Inhibitor for Acne
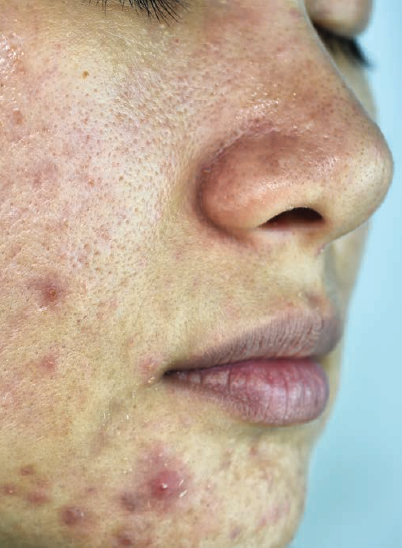 The FDA recently approved clascoterone cream 1% for the treatment of acne in patients aged 12 years or older.1 This is the first FDA-approved treatment in 40 years to target a new mechanism of action for acne.
The FDA recently approved clascoterone cream 1% for the treatment of acne in patients aged 12 years or older.1 This is the first FDA-approved treatment in 40 years to target a new mechanism of action for acne.
Clascoterone cream 1% is an androgen receptor inhibitor that is thought to compete with androgens, specifically dihydrotestosterone, for binding to the androgen receptors in sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Two phase 3 clinical trials showed clascoterone cream 1% achieved treatment success, reduced acne lesions, and had a favorable safety profile compared with vehicle.2
Clascoterine is intended for twice-daily application. The most commonly reported adverse effect was mild erythema.1 Other reported adverse effects included pruritus, burning, edema, and peeling. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression was observed in one adult participant and two adolescent participants. Elevated potassium was observed in 5% of participants, though this was also observed in 4% of participants in the vehicle group.
References
1. Cassiopea. Cassiopea receives FDA approval for Winlevi® (clascoterone cream 1%), first-in-class topical acne treatment targeting the androgen receptor. Press release. PR newswire; August 27, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2020. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cassiopea-receives-fda-approval-for-winlevi-clascoterone-cream-1-first-in-class-topical-acne-treatment-targeting-the-androgen-receptor-301119454.html
2. Hebert A, Thiboutot D, Stein Gold L, et al. efficacy and safety of topical clascoterone cream, 1%, for treatment in patients with facial acne: two phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156(6):621-630. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0465
Hyaluronic Acid Fillers Safe, Effective for Asian Patients
Two hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers with lidocaine were found to safely and effectively improve the aesthetic appearance of Asian participants seeking full-face aesthetic treatment in a recent study.
In a 24-month, noncomparative, multicenter study, the researchers evaluated the safety and efficacy of two HA fillers with lidocaine among 100 participants who underwent full-face aesthetic treatment. Participants were injected with 3 to 5 mL of HA filler with lidocaine in two to three predefined treatment areas in the upper checks, nasolabial folds, temples, nose, and chin at baseline and 12 months. The total mean volume at the first treatment was 4.7 mL and the total mean volume at the second treatment was 3.1 mL. Aesthetic improvement, participant satisfaction, assessment scales for upper checks and nasolabial folds, and safety were assessed as primary outcomes.
After 24 months, 82% of the participants were rated as aesthetically improved by both themselves and by investigators. The majority of participants (73%-90%) reported that they were satisfied with their treatment throughout the study. In addition, the researchers found upper check improvement was significantly higher 12 months after the second treatment compared with 12 months after the first treatment (≥69% vs ≥38% , respectively).
Overall, 29 treatment-related adverse events were reported by 16% of participants. All adverse events were mild (79%) or moderate (21%) in intensity. The most commonly reported ones were pain and bruising; however, tenderness at treatment sites was the most commonly documented adverse event in diary records.
Reference
Huang SH, Tsai TF. Safety and effectiveness of hyaluronic acid fillers with lidocaine for full-face treatment in Asian patients. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19(9):836-842. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5374
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Risk Factors Identified
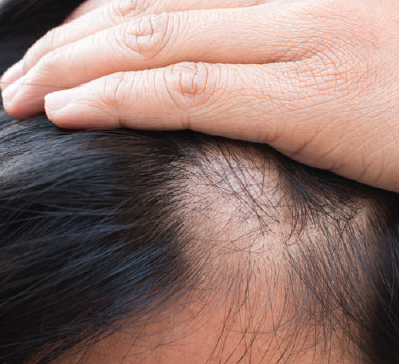 A group of researchers from Henry Ford Health System recent study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology identified several potential risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), including the use of certain hair and skin care products.
A group of researchers from Henry Ford Health System recent study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology identified several potential risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), including the use of certain hair and skin care products.
The incidence of FFA is rising worldwide, but the etiology of this type of alopecia is still unknown, the researchers wrote. They evaluated the association between FFA and demographic and exposition factors among a multiracial population in Brazil. A total of 11 referral centers participated in the study and recruited 451 participants with FFA and 451 sex-matched controls. All participants completed a thorough questionnaire that collected data on their baseline demographics, environmental exposition, diet, hormonal, allergies, and hair and skin care products.
After adjusting for sex, age, menopause, and skin color, the researchers found FFA was associated with hair straightening formalin (odds ratio [OR], 3.19); use of ordinary, nondermatologic facial soap (OR, 2.09); facial moisturizers (OR, 1.99); thyroid disorders (OR, 1.69); and rosacea (OR, 2.08). They found a negative association between FFA and smoking (OR, 0.22) and use of antiresidue/clarifying shampoo (OR, 0.35). In addition, sunscreen use was not associated with FFA.
“The association with moisturizers, ordinary facial soap, and hair straightening with formalin and the negative association with anti-residue/clarifying shampoo reinforce the possibility of an exogenous particle triggering FFA,” the researchers concluded. Recall bias was noted as a limitation of this study. n
Reference
Ramos PM, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online August 21, 2020. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.076
Which Foods Worsen or Improve HS?
 Dietary counseling may be a beneficial addition to a comprehensive hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) management plan, according to the findings of a recent study.
Dietary counseling may be a beneficial addition to a comprehensive hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) management plan, according to the findings of a recent study.
“While dietary triggers have been investigated in acne and other inflammatory follicular dermatoses, there is a paucity of data on diet and HS,” the researchers wrote. They conducted an anonymous survey to identify foods patients with HS thought exacerbated or alleviated their disease through Facebook support groups for HS and in-person HS specialty clinics.
In the survey, participants were given a list of foods and were instructed to identify whether they believed those foods worsened or improved their HS. The list included sweet foods, breads and pasta, red meat, chicken, fish, canned foods, fruits, vegetables, dairy, and high-fat foods.
According to the survey results, 32.6% of participants (237 of 728) identified foods that exacerbated their HS symptoms, whereas only 12% (89 of 744) identified foods that alleviated their HS.
Sweets (67.9%), bread/pasta/rice (51.1%), dairy (50.6%), and high-fat foods (44.2%) were the most commonly reported exacerbating foods. Foods most commonly reported to alleviate symptoms were vegetables (78.7%), fruits (56.2%), chicken (51.7%), and fish (42.7%).
“Further studies are required to evaluate the mechanistic links between diet and HS,” the researchers concluded.
Reference
Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Published online August 29, 2020. Dermatol Ther. doi:10.1111/dth.14246
Which Modalities are Effective for AKs?
A recent study published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology found certain lesion- and field-directed treatments were safe and effective for actinic keratoses (AKs), particularly among patients with multiple lesions.
“For a disease such as actinic keratosis that is associated with high rates of nonadherence and nonpersistence to treatment, real-world evidence is crucial to confirm clinical efficacy,” the researchers wrote. To better understand the real-world treatment of AKs by type and modality, they analyzed clinical and outcome data from the medical charts of 429 patients with AKs.
They found that the first treatment after diagnosis was a procedure, followed by a topical therapy. Treatment with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), ingenol mebutate (IngMeb), imiquimod (IMQ), cryotherapy alone, or cryotherapy plus one topical was associated with 66%, 69.3%, 72.5%, 72.9%, and 73% reductions in AKs, respectively. They also found that a 75% or greater clearance of AKs was achieved by 57.1%, 72.7%, 57.1%, 62.4%, and 62% of patients treated with 5-FU, IngMeb, IMQ, cryotherapy alone, or cryotherapy plus one topical, respectively.
In addition, the researchers found that treatment effectiveness was positively correlated with the number of AKs at baseline for topical and for procedural plus topical combination treatments, but not for procedural treatments alone. Specifically, patients with six or more AKs were treated with topicals or with a combination of a procedure plus a topical, which was associated with higher rates of complete clearance compared with a procedure alone.
Cryotherapy was associated with more adverse reactions (9.7%), whereas field-directed treatment (18.5%-43.1%) and combination cryotherapy plus topical treatment (21.3%) were associated with more local skin reactions.
“This study highlights the greater utility and benefits of field-directed topical treatments for AKs, such as IngMeb, 5-FU, and IMQ, especially when a greater number of AKs over a larger field size are involved,” the researchers concluded. “Future large-scale, long-term, real-world studies may further our understanding of the most effective management.”
The limitations of this retrospective study were the limited duration and small population size. n
Reference
Hansen JB, Larsson T, Dunkelly-Allen N, Veverka KA, Feldman SR. Real-world effectiveness and safety of field- and lesion-directed treatments for actinic keratosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19(8):756-762. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5123





















