An Unusual Approach for Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome Due to Isolated Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations
Tahir Bezgin, MD1; Aziz Inan Celik, MD1; Nart Zafer Baytugan, MD1; Suleyman Karakoyun, MD, PhD2,3; Metin Cagdas, MD, PhD1
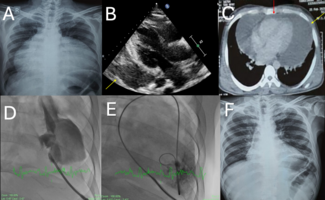
A 27-year-old man presented to the emergency department with complaints of syncope, dyspnea, and fatigue. Physical examination revealed left-sided mild hemiparesis, platypnea, and continuous murmur on right middle lobe lung auscultation. Pulse oximetry analysis revealed worsening hypoxemia during the upright position (78%) and ameliorating hypoxemia during the supine position (84%). Thoracic computed tomographic angiography (CTA) demonstrated multiple pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (PAVM) (Figure A,B). We suspected hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. However, the patient did not meet the other diagnostic criteria except for PAVMs. Pulmonary angiography was performed to demonstrate the PAVMs in detail, and it was determined that the right-sided malformations were enormous, while the left-sided malformations were relatively small (Figure C, D, E, F, Video ).
The heart team decided to occlude the right-sided PAVMs by percutaneous approach. Since there was no vascular plug in our laboratory, we decided and occluded the malformations with the atrial septal defect (ASD) closure devices (Figure E, F). At a 5-month follow-up, the patient’s capillary oxygen saturation reached 94% in the supine position and 91% in an upright position, and the symptoms were completely relieved.

Affiliations and Disclosures
From the 1Department of Cardiology, Gebze Fatih State Hospital, Heart Center, Kocaeli, Turkey; 2Department of Cardiology, Akademi Hospital, Kocaeli, Turkey; 3Faculty of Health Sciences, Kocaeli Health and Technology University, Kocaeli, Turkey
Disclosures: The authors report no financial relationships or conflicts of interest regarding the content herein.
Address for Correspondence: Aziz Inan Celik, MD, Osman Yilmaz neighborhood, Istanbul street, 127, 41400, Department of Cardiology, Gebze Fatih State Hospital, Heart Center, Kocaeli, Turkey, Email: azizinanmd@hotmail.com