May 2019 Table of Contents
Original Contributions
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Femoropopliteal Arterial Dissections Post Flex Vessel Prep and Adjunctive Angioplasty: Results of the Flex iDissection Study
Nicolas W. Shammas, MD, MS; W. John Shammas, BS; Susan Jones-Miller, MS; Qais Radaideh, MD; Gail A. Shammas, BSN, RN
Luminal gain post balloon angioplasty (PTA) is in part due to the occurrence of dissections. The depth and extent of dissections, however, can influence the short- and long-term outcomes of a procedure. Focal force and scoring balloons have been used to reduce angiographic dissections post PTA. Our aim was to examine the role of the Flex Vessel Prep system (VentureMed Group), a dynamic, microincision, non-balloon based system, prior to PTA in reducing or limiting severe dissections.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):121-126.
Coronary Artery Disease
Percutaneous Left Atrial Appendage Closure in Patients With Inferior Vena Cava Filters: A Case Series
Faten El Ayech, MD*; Julien Ternacle, MD, PhD*; Selim Boudiche, MD; Romain Gallet, MD, PhD; Madjid Boukantar, MD; David Hamon, MD; Annabelle Nguyen, MD; Elisabeth Riant, MD; Gauthier Mouillet, MD; Emmanuel Teiger, MD, PhD; Nicolas Lellouche, MD, PhD *Joint first authors.
Percutaneous procedures through femoral access in patients with an inferior vena cava filter may be at risk of complications. We evaluated the feasibility and safety of left atrial appendage closure through femoral access in patients previously implanted with an inferior vena cava filter. LAA closure was successfully implanted in all cases using an Amulet device in 3 patients and a Watchman device in 2 patients.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):128-132.
Chronic Total Occlusion
Frequency and Outcomes of Ad Hoc Versus Planned Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Multicenter Experience
Yader Sandoval, MD; Peter Tajti, MD; Aris Karatasakis, MD; M. Nicholas Burke, MD; Barbara A. Danek, MD; Dimitri Karmpaliotis, MD, PhD; Khaldoon Alaswad, MD; Farouc A. Jaffer, MD, PhD; Robert W. Yeh, MD; Mitul Patel, MD; Ehtisham Mahmud, MD; Oleg Krestyaninov, MD; Dmitrii Khelimskii, MD; James W. Choi, MD; Anthony H. Doing, MD; Catalin Toma, MD; R. Michael Wyman, MD; Barry Uretsky, MD; Santiago Garcia, MD; Michalis Koutouzis, MD; Ioannis Tsiafoutis, MD; Elizabeth Holper, MD; Jeffrey W. Moses, MD; Nicholas J. Lembo, MD; Manish Parikh, MD; Ajay J. Kirtane, MD; Ziad A. Ali, MD; Darshan Doshi, MD; David E. Kandzari, MD; Judit Karacsonyi, MD; Bavana V. Rangan, BDS, MPH; Craig Thompson, MD; Subhash Banerjee, MD; Emmanouil S. Brilakis, MD, PhD
For patients needing coronary chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a planned, staged intervention has been recommended by experts. Ad hoc CTO-PCI, however, occurs in practice. Our study examined the frequency, characteristics, procedural techniques, and outcomes of 2282 patients who underwent ad hoc vs planned CTO-PCI between 2012 and 2017.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):133-139. Epub 2019 January 15.
Advances in Venous Therapies
Upper-Extremity Venous Access for Children and Adults in Pediatric Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
Jess T. Randall, MD; Osamah Aldoss, MD; Asra Khan, MD; Melissa Challman; Gurumurthy Hiremath, MD; Athar M. Qureshi, MD; Manish Bansal, MD
Traditional approaches to pediatric cardiac catheterization have relied on femoral venous access. Upper-extremity venous access may enable cardiac catheterization procedures to be performed safely for diagnostic and interventional catheterizations. The objective of this multicenter study was to demonstrate the feasibility and safety of upper-extremity venous access in a pediatric cardiac catheterization laboratory.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):141-145. Epub 2019 February 15.
Coronary Artery Disease
A Long-Term Single-Center Registry of 6893 Patients Undergoing Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With the Xience Everolimus-Eluting Stent
Daniela Trabattoni, MD; Franco Fabbiocchi, MD; Piero Montorsi, MD; Stefano Galli, MD; Paolo Ravagnani, MD; Giuseppe Calligaris, MD; Giovanni Teruzzi, MD; Luca Grancini, MD; Sarah Troiano, MD; Cristina Ferrari, MD; Antonio L. Bartorelli, MD
The safety and effectiveness of the everolimus-eluting stent (EES) have been previously demonstrated. Our aim was to assess very long-term performance and outcomes of the EES in a real-world population. This single-center registry prospectively enrolled 6893 patients undergoing elective coronary intervention with the EES over a decade. Clinical follow-up was performed at 1 year and then yearly thereafter.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):146-151. Epub 2019 January 15.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Predictors of Extended Postoperative Length of Stay After Uncomplicated Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Alexis K. Okoh, MD; Setri Fugar, MD; Nathan Kang, MS; Nicky Haik, BA; Michael Choi, BA; Marc Cohen, MD; Bruce Haik, MD; Chunguang Chen, MD; Mark J. Russo, MD, MS
This study aimed to identify predictors of extended postoperative length of stay after uncomplicated transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Non-transfemoral approach, non-elective admission, female sex, low mean transaortic gradient, presence of chronic renal failure, and pulmonary hypertension were among the factors examined.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):153-158.
Online Exclusives
Brief Communication
Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy of Calcified Coronary Lesions in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: First-in-Man Experience
Bernard Wong, MBChB; Seif El-Jack, MBBS; Ruth Newcombe, DCR; Timothy Glenie, MBChB; Guy Armstrong, MBChB; Aleksandar Cicovic, MBChB; Ali Khan, MBBS
We present the first cases of Shockwave intravascular lithotripsy (S-IVL; Shockwave Medical), a novel coronary calcium modification device, being used in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The 3 presented cases include an upfront use of S-IVL in a right coronary artery, an in-stent restenosis, and a community cardiac arrest/STEMI equivalent where S-IVL was used as a bail-out technique to facilitate stent delivery in a tortuous calcified vessel.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E73-E75.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Impact of Valve Over-Sizing After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation With a Self-Expanding Valve: A Multislice Computed Tomography Study
Maria Drakopoulou, MD; Konstantinos Toutouzas, MD; Konstantinos Stathogiannis, MD; George Latsios, MD; Skevos Sideris, MD; Maria Xanthopoulou, MD; Vicky Penesopoulou, MD; George Trantalis, MD; Andreas Synetos, MD; Angelos Papanikolaou, MD; Constantina Aggeli, MD; Manolis Vavuranakis, MD; Dimitrios Tousoulis, MD
In transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), prosthesis oversizing prevents paravalvular regurgitation. Strategies of oversizing for self-expanding bioprostheses are not well established at present. Our study aim was to define the optimal value of valve sizing for reducing paravalvular regurgitation after TAVI.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E76-E82.
Review
Transradial Approach to Coronary Angiography and Percutaneous Intervention in Patients With Dextrocardia
Gregory J. Sinner, MD; Bennet George, MD; Adrian W. Messerli, MD
Patients with dextrocardia present unique challenges in the catheterization laboratory. Variable coronary artery anatomy impacts percutaneous access, catheter selection and manipulation, and image acquisition. This is a review of all published reports of radial artery access for diagnostic and/or therapeutic coronary interventions in patients with dextrocardia. We conclude that the radial approach is safe and effective in these patients and should be used without hesitation. In addition, interventionalists should consider use of multipurpose catheters and possess an understanding of how mirror-image fluoroscopy impacts catheter manipulation.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E83-E88.
Clinical Images
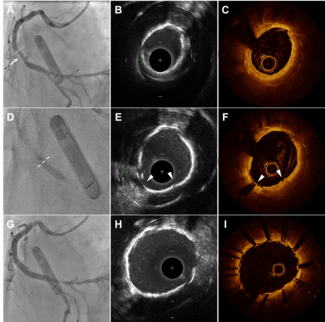
Coronary Stent Fracture: Still a Cause of Stent Failure
Vitor Pazolini, MD; Carlos Campos, MD, PhD; Adriano Caixeta, MD, PhD
In the present case, multimodality images facilitated our understanding of the mechanism behind the patient’s restenosis; a technique using optical coherence tomography with three-dimensional reconstruction allowed the clear identification and extent of stent fracture as well as its subsequent optimal treatment.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E89-E90.
Clinical Images
Coronary Artery Thrombosis in a Neonate With Critical Aortic Stenosis
Aphrodite Tzifa, MD(Res), FRCPCH; Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD; Konstantinos Patris, MD
To our knowledge, this is the first report describing coronary artery occlusion in a pediatric patient with critical aortic stenosis. We hypothesize that thrombus formation was due either to in situ fresh thrombus formation resulting from low cardiac output or secondary to an atrial arrhythmia in the presence of severe left ventricular diastolic dysfunction that may have occurred during the flight to our facility.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E91-E92.
Clinical Images / Peripheral Vascular Disease
Optical Coherence Tomography Evaluation of Superficial Femoral Artery Directional Atherectomy
Wai Kin Chi, MBChB; G.M. Tan, MBChB; Chi Yuen Chan, MBChB; Bryan P Yan, MBBS, MD
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of optical coherence tomography evaluation of superficial femoral artery atherectomy in a patient from the Asia-Pacific region. We demonstrate the feasibility of this technique in Chinese populations.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E93-E94.
Clinical Images
Right Atrial, Right Ventricular, Superior Vena Cava Dissection Caused by Swan-Ganz Catheter Placement
Nicholas Suraci, MD; Pedro Garcia, MD; Christos Mihos; Gerald Rosen, MD; Orlando Santana, MD
This case involves Swan-Ganz catheter placement in a patient who developed cardiogenic shock, possibly due to the catheter dissecting the intimal lining of the superior vena cava and endocardium.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E95.
Clinical Images
A Hydrophilic-Wire Induced Vascular Perforation Causing Mediastinal Hematoma During Transradial Coronary Intervention
Jincheng Guo, MD and Jiahui Song, MD
This is the first reported case of evidence of a hydrophilic wire traveling into a small branch and inducing perforation; this case highlights the need for fluoroscopically guided hydrophilic wire manipulation. Prompt treatment of such perforations is the best course of action.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(5):E96.
Clinical Images
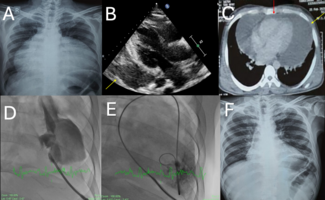
TAVR Complicated by Thoracic Aortic Perforation and Intussusception of the Right Iliac: Report of Successful Emergent Management With Endovascular Techniques
Ashleigh Long, MD, PhD and Paul Mahoney, MD
Percutaneous approaches have become routine in transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Despite numerous advantages, vascular complications associated with percutaneous access can occur during and after TAVR, and increase morbidity and mortality significantly. Effective management of potentially catastrophic vascular complications often requires prompt recognition, diagnosis, and management by multidisciplinary teams.