March 2020 Table of Contents
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Hemodynamic Outcome and Valve Durability Beyond Five Years After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Marie-Isabel Murray, MD; Eileen Hofmann, MD; Roberta De Rosa, MD; Silvia Mas-Peiro, MD; Philipp Seppelt, MD; Thomas Walther, MD; Andreas M. Zeiher, MD; Stephan Fichtlscherer, MD; Mariuca Vasa-Nicotera, MD
The aim of this study was to evaluate hemodynamic outcome, structural valve deterioration, and bioprosthetic valve failure beyond 5 years after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Demographic, procedural, and outcome data were obtained from all patients treated with TAVR at our institution from 2006 to 2012.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):82-87.
Mitral Valve Disease
Afterload Mismatch After MitraClip Implantation: Intraoperative Assessment and Prognostic Implications
Siddarth Jogani, MD; Caroline M. Van de Heyning, MD, PhD; Bernard P. Paelinck, MD, PhD; Dina De Bock, MD; Pieter Mertens, MD; Hein Heidbuchel, MD, PhD; Marc J. Claeys, MD, PhD
The aim of this study was to evaluate the acute hemodynamic effects after MitraClip implantation and to identify predictors of afterload mismatch and its prognostic implications. Acute hemodynamic effects were assessed intraoperatively by right heart catheterization and transesophageal echocardiography in 62 patients with severe mitral regurgitation.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):88-93. Epub 2020 February 5.
Chronic Total Occlusions
High-Risk Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Interventions Assisted With TandemHeart
Saroj Neupane, MD; Mir Basir, DO; Mohammed Alqarqaz, MD; William O’Neill, MD; Khaldoon Alaswad, MD
Hemodynamic support is increasingly utilized to avoid hemodynamic collapse during high-risk chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). We retrospectively evaluated intermediate-term procedural and clinical outcomes in consecutive patients undergoing TandemHeart-assisted CTO-PCI at our institution from April 1, 2016 to January 30, 2019.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):94-97. Epub 2019 December 15.
Peripheral Vascular Disease
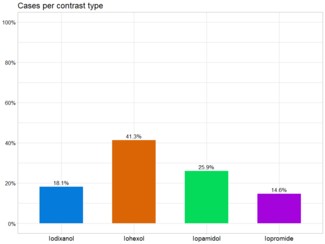
Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging Versus Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients With Peripheral Vascular Disease
George Pliagas, MD; Fadi Saab, MD; Konstantinos Stavroulakis, MD; Theodosios Bisdas, MD, PhD; Sara Finton, BSN; Carmen Heaney, BSN; Theresa McGoff, BSN; Kimberly Hardy, CST; George Adams, MD; J.A. Mustapha, MD
Historically, digital subtraction angiography (DSA) has been considered the gold standard for assessing arterial plaque morphology and vessel diameter. However, this modality provides a two-dimensional image of a three-dimensional luminal structure. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) has been incorporated into diagnostic and treatment algorithms to further characterize the arterial vessel. This study compared visual estimation of vessel diameter by DSA with IVUS.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):99-103.
Coronary Artery Disease
ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Contemporary Management From the Multicenter START Registry
Meena Zareh, MD; Jeffrey J. Rade, MD; Joseph L. Thomas, MD; Atman Shah, MD; Ankush Chhabra, MD; Jordan Prutkin, MD; Zach Shinar, MD; Michael Abraham, MD; Nathan Deal, MD; Dick Kuo, MD; David Pearson, MD, MS, MBA; Lee Garvey, MD; David Lange, MD; Timothy D. Henry, MD; Shoma Desai, MD; Henry Kim, MD; Stuart Swadron, MD; Han Tun, MBBS, MPH; David M. Shavelle, MD
Recent studies suggest that primary PCI and targeted temperature management (TTM) improve outcomes in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) complicated by out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). The objective of this study was to evaluate a contemporary series of patients with STEMI and OHCA to characterize treatment approaches and predictors of neurologic outcomes.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):104-109. Epub 2020 January 15.
Coronary Artery Disease
Long-Term Outcomes of Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease: Comparison of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Kai Song, MD; Moo Hyun Kim, MD; Jia Xin Li, MD; Soo Jin Kim, MD; Kwang Min Lee, MD; Young-Rak Cho, MD; Jong Sung Park, MD; Tae Ho Park, MD; Young Dae Kim, MD; Michael S. Lee, MD
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is the standard of care for unprotected left main coronary artery (ULMCA) disease. Contemporary randomized trials have reported conflicting results with the two revascularization strategies for the treatment of ULMCA disease at intermediate-term follow-up. We compared the long-term outcomes of CABG with PCI for ULMCA disease in a real-world population.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):111-116. Epub 2020 January 15.
Coronary Artery Disease
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With the Agent Paclitaxel-Coated Balloon: A Real-World Multicenter Experience
Gianmarco Iannopollo, MD; Francesco Giannini, MD; Francesco Ponticelli, MD; Beniamino Pagliaro, MD; Giorgio Tzanis, MD; Guglielmo Gallone, MD; Matteo Montorfano, MD; Antonio Colombo, MD; Alessandro Durante, MD
The Agent paclitaxel-coated balloon is a new drug-coated balloon (DCB) with few available real-world data. Our study assessed the safety and efficacy of the Agent DCB during PCI in different coronary lesion types in a prospective registry that included patients from three Italian centers between September 2014 and March 2018.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):117-122. Epub 2020 February 11.
Original Contribution
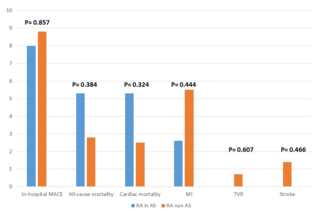
Cardiovascular Risk Stratification for Patients Treated With Drug-Eluting Stents: Development and Validation of the DESIRE Score
Adriana Costa Moreira, MD; Amanda Sousa, MD, PhD; Jose de Ribamar Costa, Jr, MD, PhD; Ricardo Costa, MD, PhD; Lucas Damiani, MS; Cantídio Campos Neto, BS, PhD; Galo Maldonado, MD; J. Eduardo Sousa, MD, PhD
We developed a risk score to estimate the risk of major adverse cardiac event (MACE) during the in-hospital and long-term follow-up periods after PCI with drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E49-E59.
Brief Communication
The Impact of a Chronic Total Coronary Occlusion on Outcomes of Patients With an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: Insights From the EXPLORE Trial
Anna van Veelen, MD; Ivo M. van Dongen, MD, PhD; Joëlle Elias, MD, PhD; José P.S. Henriques, MD, PhD
A chronic total occlusion may increase the risk of appropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) therapy. Therefore, we evaluated all patients who received an ICD during 5-year follow-up in the EXPLORE trial.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E60-E62.
Review
Solving Challenging Situations and Complications in Everyday Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Using Chronic Total Occlusion Techniques
Lorenzo Azzalini, MD, PhD, MSc*; Georgios Tzanis, MD, PhD*; Kambis Mashayekhi, MD; Barry F. Uretsky, MD; Soledad Ojeda, MD, PhD; Manuel Pan, MD, PhD; Stephane Rinfret, MD, MS; Alexandre Avran, MD; Khaldoon Alaswad, MD; Masahisa Yamane, MD; Dimitri Karmpaliotis, MD, PhD; Emmanouil S. Brilakis, MD, PhD; Mauro Carlino, MD; Luiz F. Ybarra, MD, PhD, MBA *Joint first authors
The challenging nature of CTO interventions involves regularly dealing with support-related issues, uncrossable/undilatable lesions, manipulation of equipment in the subadventitial space, and the treatment of complications such as perforation and equipment loss or entrapment. We discuss an armamentarium of techniques routinely used in CTO-PCI that can also be utilized in interventions for non-occlusive coronary artery disease and have the potential to improve the efficacy and safety of these procedures.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E63-E72.
Clinical Images
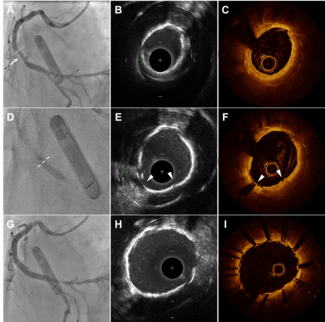
An Unusual Entity: Woven Coronary Artery Anomaly
María. T. López-Lluva, MD; José Abellán-Huerta, MD, PhD; Ignacio Sánchez-Pérez, MD; Pedro Pérez Díaz, MD; Fernando Lozano Ruíz-Poveda, MD, PhD
The recognition of woven coronary artery anomaly is difficult because of its rare nature. Optical coherence tomography imaging is challenging due to the tortuosity of the channels; however, it is crucial not only for the differential diagnosis but also to guide the treatment approach.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E73.
Clinical Images
Bilateral Hand Wasting After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Bhartendu Chandra, MD and Vijay K. Sharma, MD
Open surgical harvesting of the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) is believed to increase the risk of injury to the brachial plexus. We believe that this approach probably aggravated the neurological damage in our patient. Proper positioning, thoracoscopic harvesting of LIMA, and avoiding prolonged and excessive traction on the rib cage could have reduced the risk of this injury.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E74.
Clinical Images
Superior Vena Cava Stent Migration Into the Right Atrium
Nicholas Suraci, MD; Christos Mihos; Sebastian Baquero, MD; Orlando Santana, MD
Possible stent migration was suspected in this case and confirmed on transesophageal echocardiography. The patient underwent successful stent removal with snaring, as well as subsequent placement of another stent in the superior vena cava without further complications.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E75.
Clinical Images
The Venovo Venous Stent in Pregnancy
Andrew N. Shammas, BS, OMS; Nicolas W. Shammas, MD, MS; Mary F. Knowles, RVT; Lori Christensen, BS, RN
We present the case of a young woman who became pregnant following placement of a Venovo venous stent (BD/Bard) in her left common iliac vein. Our case illustrates the safety of the Venovo stent during pregnancy. This needs further validation with a larger registry.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E76-E77.
Clinical Images
Role of StentBoost in Successful Guidewire Recrossing
Kewal Kanabar, MD; Krishna Prasad, MD; Krishna Santosh, MD; Navjyot Kaur, MD; Prashant Panda, MD; Yash Paul Sharma, MD
In this difficult case, StentBoost (Philips Medical Systems) demonstrated abluminal passage of the guidewire through the proximal stent struts.
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2020;32(3):E78.
Clinical Images
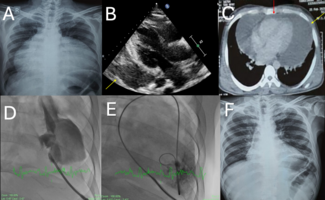
Multimodality Imaging of Purulent Pericarditis: Hints to Speed up Diagnosis and Promote Healing
Gianni Dall’Ara, MD, PhD; Simone Longhi, MD, PhD; Simone Grotti, MD; Giorgio Noera, MD; Murad H.M. Essatari, MD; Cristina Bachetti, MD; Fabio Tarantino, MD; Marcello Galvani, MD
Purulent pericarditis is rare and usually associated with pneumonia, bacteremia, immunosuppression, and thoracic surgery. A timely diagnostic pericardiocentesis with dedicated maneuvers to improve the effectiveness of drainage and pericardial fibrinolytic rinsing can improve prognosis and prevent a surgical pericardiectomy. Imaging offers useful clues for a more aggressive approach.