Large Right Coronary Artery Aneurysm
Antonio E. Smith, MD; Said Ashraf, MD; Tanveer Mir, MD; Kartik Kumar, MD; Kendall Bell, MD; Tomo Ando, MD; Frank A. Baciewicz, MD
J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2019;31(11):E339.
Key words: cardiac imaging, coronary angiography, giant coronary artery aneurysm
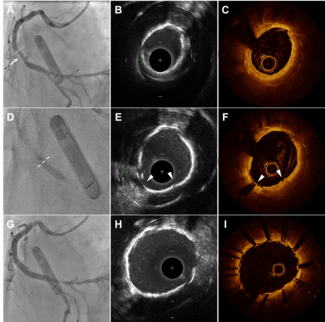
A 66-year-old male with end-stage renal disease presented with chest pain, dyspnea, and hypotension. Cardiac catheterization was negative for tamponade, but there was a large saccular aneurysm in the mid right coronary artery (Figure 1; Video 1). Saphenous vein coronary bypass graft was utilized by attaching the proximal end of the graft to the aorta and distal end to the right coronary artery distal to the aneurysm. The aneurysm was ligated to avoid risk of rupture.
Giant (>2 cm in diameter) coronary artery aneurysm (CAA) is a rare incidental finding on coronary angiography. Right coronary artery is the most common site involved. Occasionally, giant CAA is symptomatic, depending upon location and size. It can present as stable or unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and (rarely) sudden death.
Complications of CAA include thrombosis and distal embolization, rupture, and vasospasm. The natural history and prognosis remain obscure. Controversy persists regarding the use of surgical or medical management.
Surgical approach is thought to be safer and more reliable for repair of CAA/pseudoaneurysm. The indications for the surgical treatment of CAA in general are severe coronary stenosis, complications (such as fistula formation), compression of the cardiac chambers, high likelihood of rupture (such as rapidly increasing size of the aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm), and any type of aneurysm developing after coronary intervention.
From Wayne State University/Detroit Medical Center Internal Medicine, Detroit, Michigan.
Disclosure: The authors have completed and returned the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The authors report no conflicts of interest regarding the content herein.
The authors report that patient consent was provided for publication of the images used herein.
Manuscript accepted March 1, 2019.
Address for correspondence: Antonio E. Smith, MD, Wayne State University/Detroit Medical Center Internal Medicine, 4201 St Antoine, Detroit, MI 48201. Email: asmith@med.wayne.edu