Bulletin Board - February 2013
FDA NEWS
FDA Requires Manufacturers of Zolpidem-Containing Sleeping Pills to Lower Recommended Doses
On January 10, 2013, the FDA announced a new requirement to lower the recommended doses of Ambien, Ambien CR (extended-release), Edluar, Zolpimist, and their generic equivalents, all of which are sleep drugs that contain zolpidem as their active ingredient. High serum levels of zolpidem have been found in some patients the morning after use, which may impair the ability to perform activities that require alertness, such as walking, thereby increasing the risk of falls and other injuries. The risk for next-morning impairment was highest in patients receiving extended-release formulations of these agents, rather than immediate-release products.
Because women eliminate zolpidem at a slower rate than men, the FDA has required the recommended dosage of zolpidem for women to be lowered from 12.5 mg to 6.25 mg for extended-release products, and from 10 mg to 5 mg for immediate-release products. Although the recommended dosage has not been lowered for men, the FDA has required the drug labeling information be changed to recommend prescribing these lower doses to men as well.
The FDA is continuing to evaluate the risk of other over-the-counter and prescription insomnia drugs. Until data for these other agents become available, “professionals should prescribe, and patients should take, the lowest dose capable of treating the patient’s insomnia,” said Ellis Unger, MD, director, Office of Drug Evaluation I, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in an FDA press statement.
PRODUCT SPOTLIGHT
Award-Winning BioMask Can Protect Patients From Flu
In the United States, flu season lasts from October to May, usually peaking in January or February. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, receiving the influenza vaccine is a crucial step in reducing the risk of flu, but it only has a moderate effectiveness of about 60% against circulating flu strains, indicating a need for other protective measures. To address this need, Medline developed BioMask, which has been shown to inactivate 99.99% of laboratory-tested flu viruses within 5 minutes of contact, including imminent pandemic and seasonal strains of influenza viruses, such as H1N1, avian flu, swine flu, and H3N2; these have been the dominant flu strains in the United States for the 2012-2013 flu season.
Unlike other face masks that simply filter air, BioMask uses proprietary Ionixx technology that incorporates citric acid, copper, and zinc, all of which are natural and safe compounds, to inactivate viruses. A hydrophilic coating on the outside of the mask quickly wicks away droplets from the surface, while the low pH in the citric acid begins inactivating viruses on contact. When droplets land on the mask’s inner blue layer, the copper and zinc, which are toxic to pathogens, inactivate any remaining viruses.
The BioMask was launched under Medline’s Curad brand name and is available at major retail chains. It can also be ordered in bulk for use in medical and healthcare facilities, including nursing homes. For bulk ordering information and additional product details, visit www.medline.com
“Dr. Superman” Assesses Cognitive Function in Seconds
Tests like the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which screen geriatric patients for dementia, are a vital part of a comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA); however, they can be time consuming to administer. The MMSE alone can take up to 20 minutes, putting a strain on clinical resources. To tackle this challenge, Takeshi Ohnuma, Department of Geriatric Medicine, Tokyo Medical University, Japan, and colleagues developed a CGA called “Dr. Superman,” which can be completed within 10 minutes.
To develop Dr. Superman, 90 elderly outpatients were administered the MMSE along with one episodic memory question (ie, “What kind of food did you have last night?”). Patients were then divided into two groups: those with a normal MMSE score of ≥24 (n=42) and those with an abnormal score of ≤23 (n=48). Seven domains (ie, time orientation, place orientation, immediate memory, calculation, recall, language, spatial cognition) and episodic memory were scored separately within each group. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive predicative values were calculated for each. The data was then evaluated to determine the best combination of domains for practical use as an assessment tool.
Based on the observation of high sensitivity, specificity, or positive predicative value, the combination of “What is this year?” in the time orientation domain, “Serial 7’s twice” (counting down from 100 by sevens) in calculation recall, and the episodic memory question “What kind of food did you have last night?” was superior to other combinations (sensitivity, 93.8%; specificity, 71.4%; positive predicative value, 78.9%).
This assessment combination was then evaluated in the clinical setting on 50 outpatients. Two raters conducted the assessments, which took an average of 32 to 55 seconds to complete. There was good interrater reliability, and this combination proved to be the best and most valuable short-form screening test for cognitive decline. As such, it became the basis for the Dr. Superman geriatric assessment. The full-text article is available at www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/geriatrics/49/2/49_241/_article.
In the United States, more than 500,000 cases of Clostridium difficile (C difficile) are diagnosed annually, and there are approximately 100,000 hospitalizations. Although antibiotics and probiotics are typically used to treat C difficile, they are ineffective in preventing recurrences in about 25% of patients. Although not approved by the FDA, stool transplantation has been used successfully for more than 20 years to combat recurrences, but because this procedure requires the insertion of donor stool into the intestinal tract via a colonoscope or nasogastric tube, it can be expensive, there has been aversion to it, and various safety concerns have been raised. To improve stool transplantation safety and increase patient acceptance, a synthetic probiotic stool was recently developed.
Referred to as RePOOPulate, the synthetic stool was created by microbiologist Emma Allen-Vercoe, PhD, Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, and colleagues using purified intestinal bacterial cultures that were grown using equipment that mimics the environment of the large intestine. The 33 bacterial strains that comprise RePOOPulate were isolated from stool donated by a healthy 41-year-old woman who had not taken any antibiotics for more than a decade, and the strains were selected because they are known to be healthy.
RePOOPulate was tested in two patients with chronic C difficile infections. These patients had been treated with several rounds of antibiotics, but these treatments failed to resolve their diarrhea. After RePOOPulate was instilled in their colon via colonoscope, both patients’ symptoms completely resolved within 3 days and tests showed no trace of C difficile 6 months later. Both patients were elderly women (aged ≥70 years) and infected with a hypervirulent strain of C difficile known as polymerase chain reaction ribotype 078. Because both patients were free of C difficile at 6 months, the investigators concluded that RePOOPulate microbes are able to persist in the gut, just like the microbes from nonsynthetic transplanted stool, and not just colonize transiently, as occurs when oral probiotics are administered. In addition, because the exact composition of the bacteria administered is known and can be controlled, Allen-Vercoe noted that the stool can be modified to meet individual patients’ needs. The objective is to make the stool commercially available to treat C difficile along with other gastrointestinal conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease.
For more on RePOOPulate and the investigators’ findings, visit www.microbiomejournal.com/content/1/1/3.
Fish Oil–Enriched Diet May Reduce Pressure Ulcer Progression
Pressure ulcers are a major concern for healthcare providers caring for older and immobile patients, and they become especially challenging to treat when they develop into an open sore that can become infected. Although pressure ulcers result from constant pressure on one area, which leads to reduced blood flow and dead skin, malnourishment can also play a role in their development and progression. A 2012 interventional, controlled, randomized study conducted by Miriam Theilla, RN, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues showed that a diet enriched with omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil can reduce the progression of pressure ulcers by 20% to 25% (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22751375).
Pressure ulcers are generally categorized into one of four stages: Stage I, there are reddened areas on the skin that do not turn white when pressed; Stage II, there is partial thickness loss of the dermis, manifesting as skin blisters that form an open sore with potential reddening and irritation around the area; Stage III, there is full thickness tissue loss that manifests as an open, sunken wound with damage to the tissue below the skin; and Stage IV, there is full thickness tissue loss that deepens to expose the muscle, bones, tendons, and joints. All 40 patients included in Theilla and colleagues’ study had pressure ulcers classified as Stage II or higher. Once enrolled, patients were randomly placed into the study group, which received an enteral nutritional formula enriched with fish oil and antioxidants (n=20), or the control group, which received an isonitrogenous nutritional formula (n=20). Baseline demographics did not differ between the two groups. Patients were observed for 28 days, and wound healing was assessed using the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing on days 7, 14, and 28, whereas serum C-reactive protein levels were measured on days 0, 7, and 14.
At 14 days, the mean C-reactive protein levels decreased significantly in the study group, from 191 mg/L to 111.7 mg/L, compared with the control group, which had a decrease from 145 mg/L to 139 mg/L (P=.02). At 28 days, the mean score on the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing increased significantly in the control group, from 9.25 to 10.75, compared with the study group, which had an increase from 9.10 to 9.40 (P=.02). Based on their findings, the authors conclude that a diet enriched with fish oil might decrease the progression of pressure ulcers and reduce blood concentrations of C-reactive protein, an important indicator of nutritional status and pressure ulcer prognosis.
LTC RESOURCE
AMDA Has Released a New Version of its Antithrombotic Tool Kit
Thrombosis has numerous causes, but one of the major risk factors for this condition is immobility, as stagnant blood is prone to clotting. Because immobility is common among older adults, they are at a greater risk for developing thrombosis. At the end of 2012, AMDA–Dedicated to Long Term Care Medicine released an updated version of its antithrombotic tool kit, which outlines the latest information on antithrombotic agents and therapy and examines challenges clinicians encounter when treating frail, complex, elderly persons residing in long-term care facilities.
The 2012 revision of Antithrombotic Therapy in Long Term Care Setting outlines evidence-based practices that will enable physicians to quickly determine the best treatments for their patients with thrombosis. Discussions include a variety of important topics, such as which patients are at greatest risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT); what is the safest way to begin, titrate, and monitor warfarin therapy for a frail elderly patient; what are the best regimens to prevent and treat DVT; and what is the best antiplatelet regimen to prevent myocardial infarction or ischemic stroke. The antithrombotic tool kit includes easy-to-read tables throughout, is structured in such a way that practitioners can quickly find answers to specific thrombosis questions, and incorporates expert opinions from specialty organizations, including the American Heart Association and the American Stroke Association. The tool kit authors also collaborated with experts in geriatric cardiology, DVT prevention, and related fields to ensure accuracy and applicability of the information provided in the tool kit. When well-designed, randomized clinical trials were not available on a particular topic to enable the authors to make evidence-based recommendations, they offer best suggested practices based on the available literature and expert consensus.
The 2012 Antithrombotic Therapy in Long Term Care Setting tool kit is available for purchase at www.amda.com. The list price is $55.00 for members and $95.00 for nonmembers.
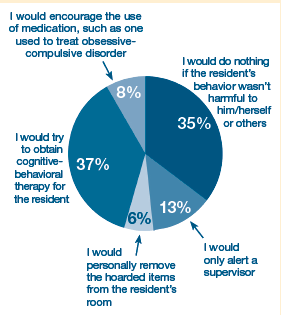
ALTC POLL RESULTS
If you observed residents of your long-term care facility hoarding items, such as possessions or medications, how would you handle the situation?